Our Process
Our Process
The ResiCare technology is compatible with a large variety of processes. We adapt our resin to the most common industrial processes but we can also develop specific resins to suit your own needs.
Prepreg
These are fibers (carbon, glass, aramid, etc.) that are supplied already impregnated with resin. This technology is most widely used in the production of aeronautical parts or parts with high mechanical and geometric constraints. During polymerization, pressure must be applied to the laminate:
- under vacuum in a membrane + oven heating
- under vacuum in a membrane + pressure from 2 to 15 bar and heating in an autoclave- under pressure in a membrane + pressure from 2 to 15 bar and heating in an autoclave.
- Under press with heating platens
- Expandable or inflatable cores in heated molds
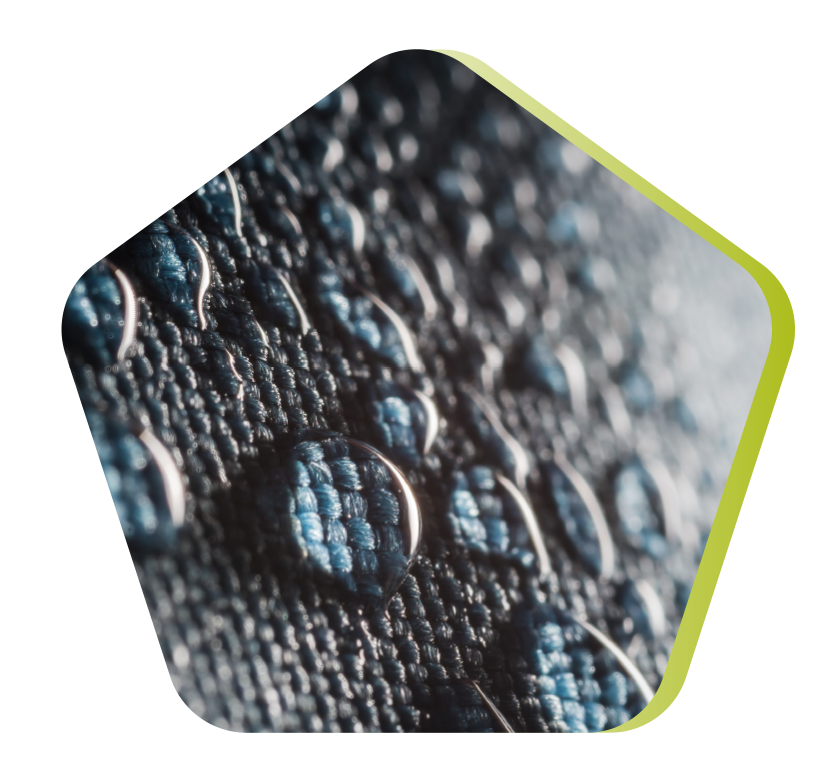

Infusion molding

Vacuum molding takes place between the mold and the rigid, semi-rigid or flexible counter-mold, depending on the technology used. The reinforcement (mat, fabric, preform) is placed inside the mold; draining fabrics and a vacuum bag are tightly placed over the tooling. A vacuum is created by a vacuum pump, and the resin is allowed to migrate through the fabrics along the entire length of the mold.
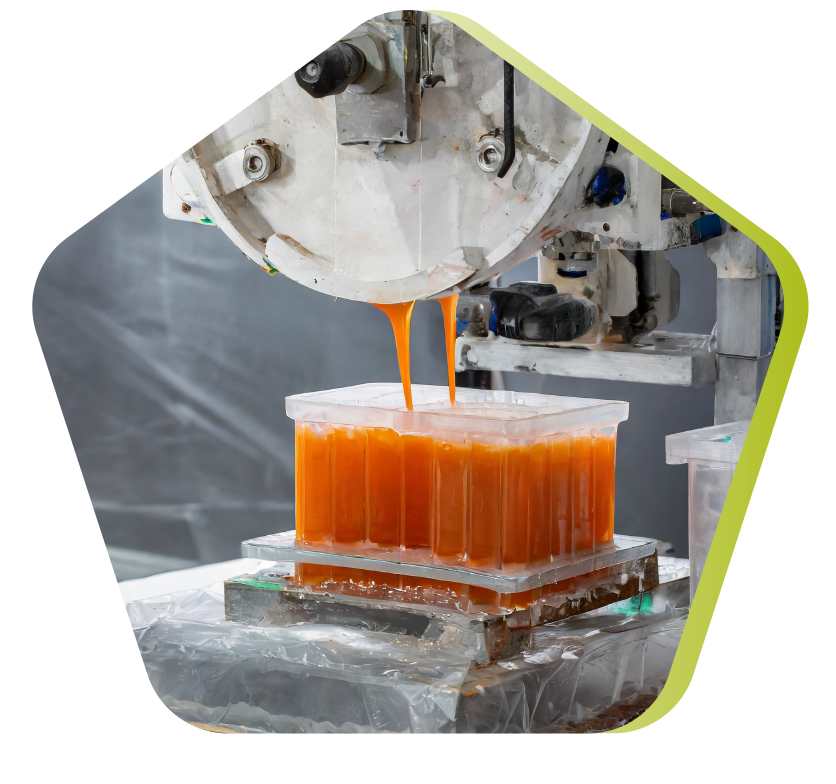
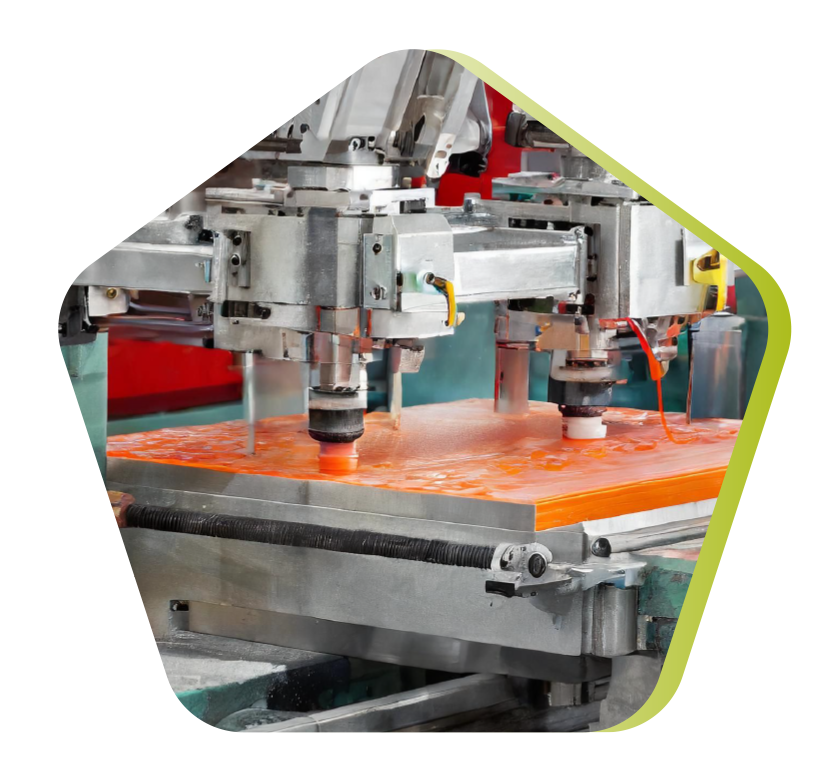
Compression molding
Compression molding is a manufacturing process in which a preheated material, usually a thermoset plastic, is placed in a mold cavity. The mold is then closed and pressure applied to force the material into the shape of the mold. The material hardens under the effect of heat and pressure, and is then demolded. Compression molding can be used to produce high-strength parts with complex shapes and large dimensions.
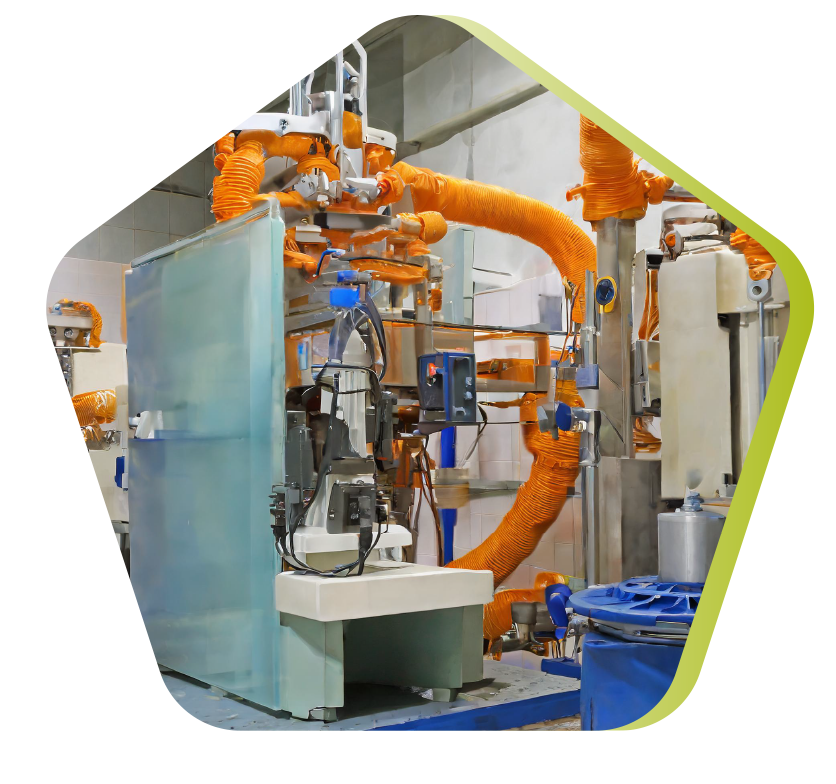

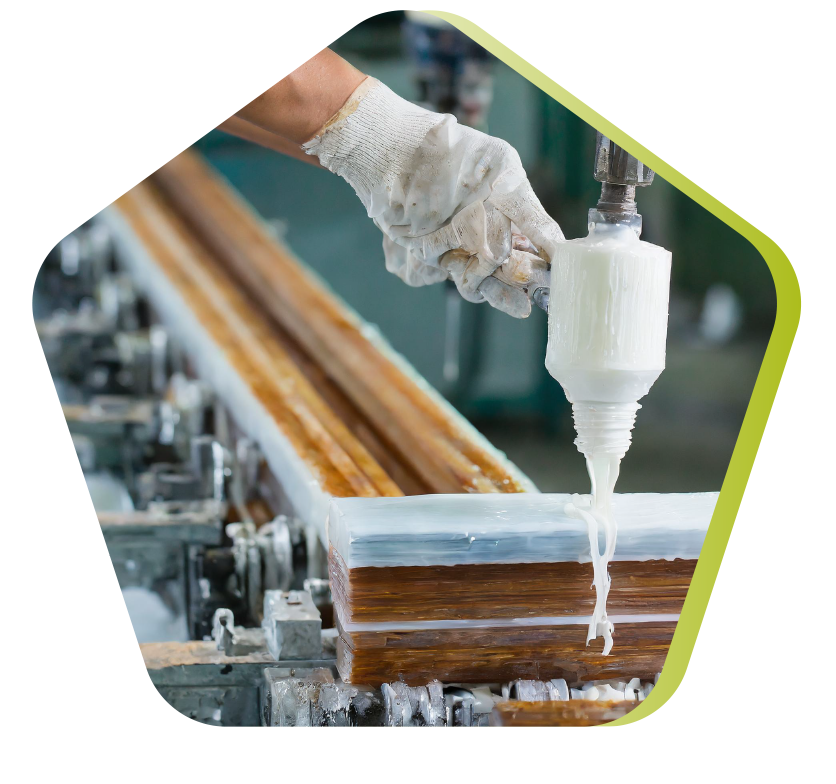
Sheet Moulding Compound
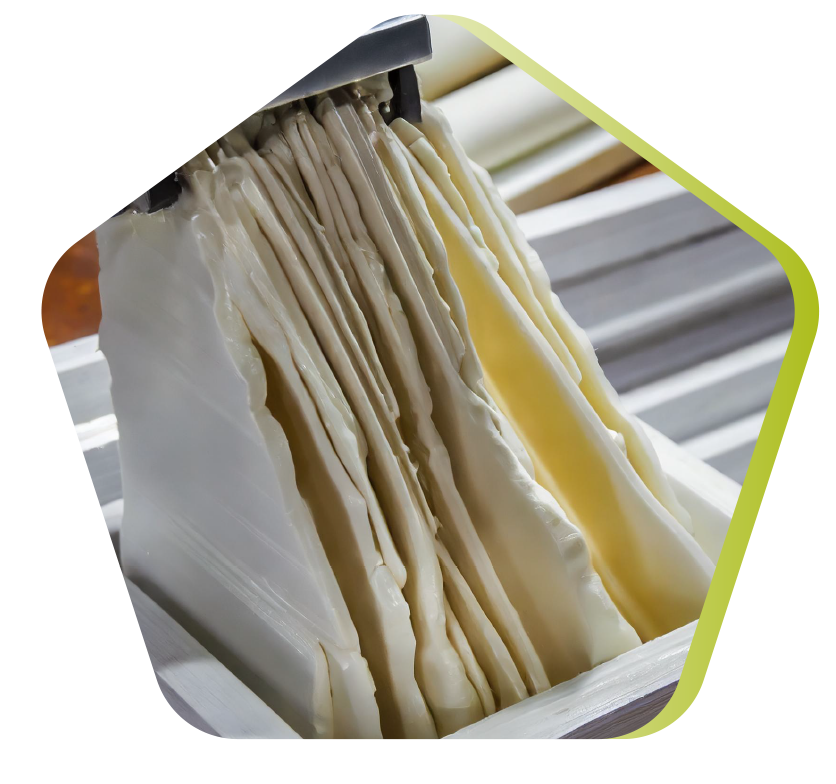

SMC (Sheet Molding Compound) prepreg mat consists of a web of cut or continuous wires, impregnated with a mixture of polyester resin, fillers and various specific additives. Cut into blanks of specified mass and dimensions, the prepreg is hot-molded (140 to 160°C) by compression between a mold and a machined steel counter-mold. The pressure (50 to 100 bar) causes the material to flow and fill the cavity. The very short curing time (depending on thickness) enables rapid demolding.
Liquid resin injection molding
RTM (Resin Transfer Molding) liquid resin injection molding takes place between a rigid mold and a rigid counter-mold. The reinforcement (mat, preform or fabric) is placed in the mold gap. Once the mold is firmly closed, the accelerated and catalyzed resin is injected under low pressure (1.5 to 4 bar) through the reinforcement until the cavity is completely filled. Once the resin has cured, the mold is opened and the part demolded.
Lay Up Moulding

Manual process for producing parts from thermosetting resins, at room temperature and without pressure. Reinforcements are placed on the mold and impregnated with liquid, accelerated and catalyzed resin. Once the resin has cured, the part is demolded and trimmed.
Pultrusion
The resin pultrusion process involves drawing reinforcing fibers (glass, carbon, etc.) through a resin bath (epoxy, polyurethane, etc.) and then through a heated die, which gives the product shape and strength. Pultrusion is used to manufacture high-quality, lightweight composite profiles with a constant cross-section.

Spray-up molding
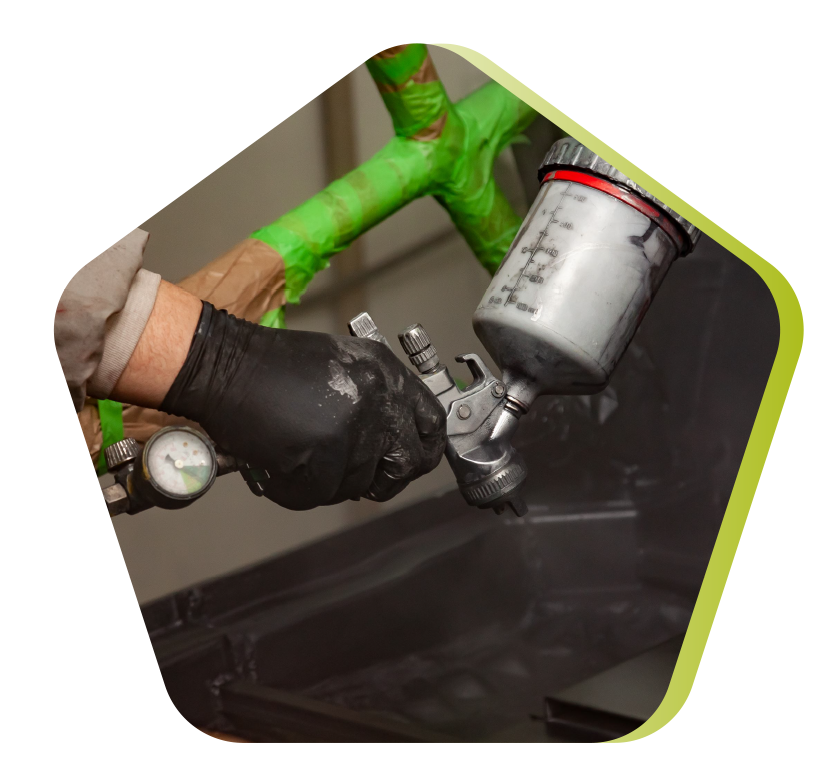

Manual or robotized process for producing parts from thermosetting resins at room temperature and without pressure. The raw materials are processed using a "projection" machine comprising :
- a device for cutting and spraying the reinforcement (roving)
- one or two guns simultaneously spraying the resin.
The cut wires and resin are sprayed onto the mold surface, then compacted and debulked using rollers and boilers.
Filament winding
The molding process limited to revolution shapes. Initially designed for the production of revolution envelopes requiring high mechanical performance, by progressively winding resin-impregnated glass yarns onto a mandrel at a given angle.

Prepreg
These are fibers (carbon, glass, aramid, etc.) that are supplied already impregnated with resin. This technology is most widely used in the production of aeronautical parts or parts with high mechanical and geometric constraints. During polymerization, pressure must be applied to the laminate:
- under vacuum in a membrane + oven heating
- under vacuum in a membrane + pressure from 2 to 15 bar and heating in an autoclave- under pressure in a membrane + pressure from 2 to 15 bar and heating in an autoclave.
- Under press with heating platens
- Expandable or inflatable cores in heated molds

Infusion molding
Compression molding is a manufacturing process in which a preheated material, usually a thermoset plastic, is placed in a mold cavity. The mold is then closed and pressure applied to force the material into the shape of the mold. The material hardens under the effect of heat and pressure, and is then demolded. Compression molding can be used to produce high-strength parts with complex shapes and large dimensions.

Compression molding
Compression molding is a manufacturing process in which a preheated material, usually a thermoset plastic, is placed in a mold cavity. The mold is then closed and pressure applied to force the material into the shape of the mold. The material hardens under the effect of heat and pressure, and is then demolded. Compression molding can be used to produce high-strength parts with complex shapes and large dimensions.

Sheet Moulding Compounds
SMC (Sheet Molding Compound) prepreg mat consists of a web of cut or continuous wires, impregnated with a mixture of polyester resin, fillers and various specific additives. Cut into blanks of specified mass and dimensions, the prepreg is hot-molded (140 to 160°C) by compression between a mold and a machined steel counter-mold. The pressure (50 to 100 bar) causes the material to flow and fill the cavity. The very short curing time (depending on thickness) enables rapid demolding.

Liquid resin infusion molding
RTM (Resin Transfer Molding) liquid resin injection molding takes place between a rigid mold and a rigid counter-mold. The reinforcement (mat, preform or fabric) is placed in the mold gap. Once the mold is firmly closed, the accelerated and catalyzed resin is injected under low pressure (1.5 to 4 bar) through the reinforcement until the cavity is completely filled. Once the resin has cured, the mold is opened and the part demolded.

Lay Up Moulding
Manual process for producing parts from thermosetting resins, at room temperature and without pressure. Reinforcements are placed on the mold and impregnated with liquid, accelerated and catalyzed resin. Once the resin has cured, the part is demolded and trimmed.

Pultrusion
The resin pultrusion process involves drawing reinforcing fibers (glass, carbon, etc.) through a resin bath (epoxy, polyurethane, etc.) and then through a heated die, which gives the product shape and strength. Pultrusion is used to manufacture high-quality, lightweight composite profiles with a constant cross-section.

Spray-up molding
Manual or robotized process for producing parts from thermosetting resins at room temperature and without pressure. The raw materials are processed using a "projection" machine comprising :
- a device for cutting and spraying the reinforcement (roving)
- one or two guns simultaneously spraying the resin.
The cut wires and resin are sprayed onto the mold surface, then compacted and debulked using rollers and boilers.

Filament winding
The molding process limited to revolution shapes. Initially designed for the production of revolution envelopes requiring high mechanical performance, by progressively winding resin-impregnated glass yarns onto a mandrel at a given angle.
To build with us the best solution adapted to your needs, let’s get in touch !
To build with us the best solution adapted to your needs, let’s get in touch !